Introduction
When we think about light, we usually picture it as a source of energy or illumination. But what if light could be more than that? What if light was also information—an invisible language plants use to grow, adapt, and thrive? Thanks to adjustable spectrum LEDs, growers now have the ability to “talk” to plants by tailoring the signals they receive. It’s no longer just about making plants grow—it’s about communicating with them.

The Evolution of Grow Lights
For centuries, plants had only one light source: the sun. Then came greenhouse cultivation, artificial lighting, and eventually the rise of High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) lamps. HPS became a grower’s favorite for its raw power, but it had limitations—too much heat, high energy bills, and poor spectral flexibility.
Enter LEDs. These lights revolutionized horticulture with efficiency, longer lifespans, and the ability to target specific wavelengths. But early LEDs were still rigid, with fixed spectrums. Adjustable spectrum LEDs changed that, turning lighting into a dynamic, customizable tool.
What Is Adjustable Spectrum?
Adjustable spectrum LEDs allow growers to fine-tune the wavelengths of light their plants receive. Instead of being stuck with one spectrum, growers can “dial in” blue, red, far-red, or UV as needed. This transforms LEDs from static fixtures into adaptive plant communication devices.
Think of it like a DJ mixing tracks. Instead of playing the same song, you adjust the beats and melodies to fit the vibe. With adjustable spectrum, growers remix light to match plant needs in real-time.
Light as a Language for Plants
Plants don’t have eyes, but they sense light in astonishing detail. Specialized proteins called photoreceptors act as their “light sensors,” interpreting signals and triggering responses.
Phytochromes detect red and far-red light to regulate flowering.
Cryptochromes and phototropins respond to blue light, guiding leaf expansion and stem elongation.
UVR8 receptors react to UV light, activating defense responses.
In short, light is not just fuel—it’s information. Adjustable spectrum LEDs are like translators, helping growers speak directly to their crops.

The Role of Different Wavelengths
Each wavelength of light tells plants something different:
Blue light encourages strong vegetative growth and compact structure.
Red light drives photosynthesis and flowering.
Far-red light influences shade avoidance and the Emerson effect, boosting efficiency when paired with red.
UV light stresses plants in small doses, triggering stronger defense compounds like flavonoids and terpenes.
By controlling these wavelengths, growers send specific “messages” to their plants.
LEDs as Plant Communication Devices
Traditional lights simply delivered energy. Adjustable spectrum LEDs go further, acting like communication devices. By adjusting ratios of blue, red, UV, and far-red, growers manipulate plant physiology with surgical precision. It’s like texting your plants instructions: “Grow taller,” “Focus on roots,” “Boost resin,” or “Prepare to flower.”
How Adjustable Spectrum Works in Practice
Modern adjustable spectrum fixtures come with tunable controls—sliders, digital apps, or integrated sensors. Some advanced systems even automate spectrum recipes, syncing with environmental data like temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels.
This isn’t just lighting—it’s a conversation between technology and biology.
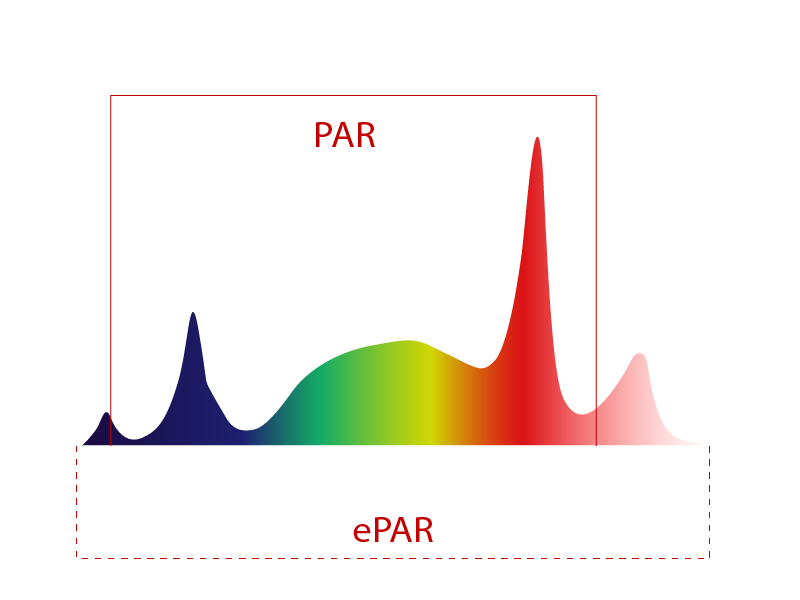
ePAR Spectrum: Extending the Range of Growth
The traditional PAR range (400–700nm) defined usable plant light for decades. But recent research introduced ePAR (extended PAR, 380–780nm), which includes far red and UV.
ePAR proved that plants utilize more wavelengths than once thought. Adjustable spectrum LEDs that cover ePAR give growers the ability to unlock hidden growth potential.
Applications in Different Growth Stages
Different stages demand different “light recipes”:
Seedlings & Clones: Higher blue light for compact, strong growth.
Vegetative Stage: Balanced blue and red to encourage leafy expansion.
Flowering & Fruiting: Red and far-red dominate to maximize bud density, fruit set, and yield.
Adjustable spectrum allows smooth transitions between these recipes, mimicking nature but with more control.
Plant Stress and Defense Mechanisms
Plants in the wild face UV radiation, fluctuating light, and competition. By simulating these stressors with spectrum tuning, growers can trigger natural defense responses.
For example, small doses of UV increase secondary metabolites, enhancing aroma, flavor, and cannabinoid production. Essentially, adjustable spectrum gives growers a way to “coach” plants into building resilience and producing higher-value compounds.
Communication in Greenhouse and Indoor Farming
In greenhouses, adjustable spectrum helps balance sunlight with supplemental LEDs like Flexstar Linear Toplights. In vertical farms, where space is limited, spectrum steering ensures uniform growth across layers.
Here, light becomes not just an energy source but a tool for crop steering—guiding plants toward desired outcomes, whether that’s yield, potency, or flavor.
Advantages of Adjustable Spectrum LEDs
Energy Efficiency: Delivering only the light plants need.
Precision Farming: Tailored recipes for different crops.
Higher Yields: Optimized photosynthesis and morphology.
Quality Boost: Enhanced taste, aroma, cannabinoids, or nutraceuticals.
Versatility: One fixture adapts to many crops and conditions.
Conclusion
Light is no longer just illumination—it’s communication. With adjustable spectrum LEDs, growers can send targeted signals that guide plants toward better growth, resilience, and quality. By rethinking light as information, we open the door to a smarter, more sustainable future for farming.
